A Common Access Card (CAC) is the standard identification for Active Duty uniformed service personnel, Selected Reserve, Department of Defense civilian employees, and eligible contractor personnel. It enables physical access to buildings, computer networks, and systems while providing two-factor authentication, digital security, and data encryption. CAC technology combines what you have (the card) and what you know (a PIN). This enables rapid authentication and significantly improves physical and logical security.
A CAC Card is roughly the size of a credit card and contains 144K of data storage and memory. The CAC has the ability to provide rapid authentication and enhance security for both physical and logical access. It does not contain sensitive information such as passwords or highly personal medical or financial data, which are stored separately.
The card is issued to active duty United States uniformed service personnel, selected reserve, National Guard, United States Department of Defense civilian employees, United States Coast Guard civilian employees, and eligible DoD contractor personnel. It also functions as the principal card for access to government buildings and for use on government defense computer networks and systems, satisfying a federal requirement for two-factor authentication.
How to Use Common Access Card?
The CAC is the primary card for physical access to buildings and controlled spaces, and it enables access to DoD computer networks and systems. The CAC satisfies two-factor authentication, and it provides enhanced security by requiring the use of a pin number to activate the card.
This task allows you to set up AppScan Enterprise so users can log in with their CAC cards without providing a username and password. The CAC Authentication feature uses PKI authentication and encryption to verify the user’s identity over an SSL connection. This feature is designed to work with the smart card middleware ActivClient, which is installed on the user’s CAC-compatible device.
The CAC is an advanced ID card that protects users against tampering, counterfeiting, and exploitation. It can be easily used by putting it in a CAC reader and entering the associated pin code. It is also resistant to spoofing and uses public key infrastructure to validate the user’s identity.
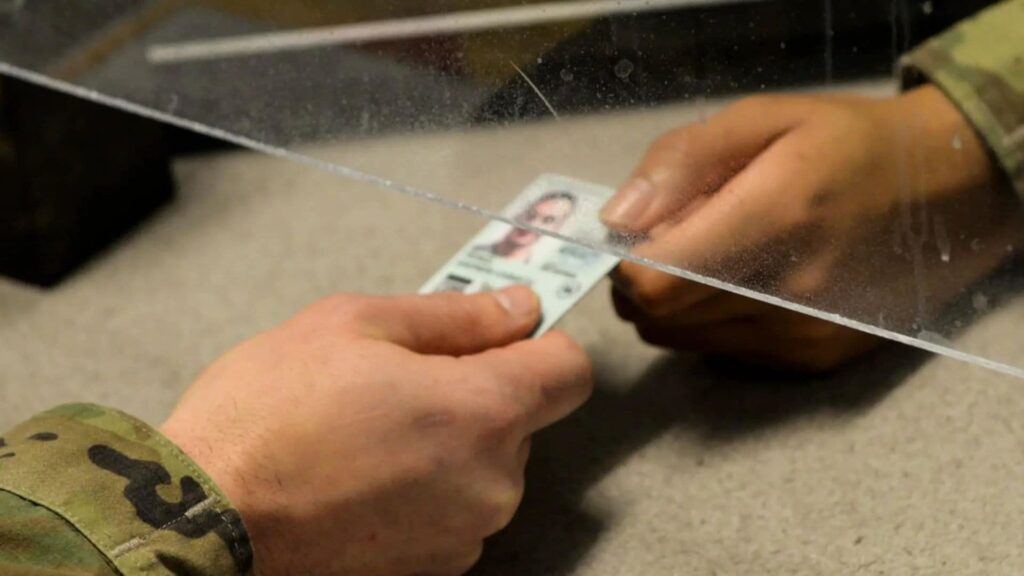
How to Renew the Common Access Card?
The CAC contains a microprocessor with personal information, cryptographic keys, and digital certificates. The card can also store a user’s PIN to help protect the information on it from being stolen. For this reason, it’s important to keep your card secure and report it immediately if lost or stolen.
You can renew your CAC by visiting a DEERS or ID Card Office at your base or completing an online request through the ID Card Office Online. The online system allows you to bypass the in-person wait time or scheduling challenges of walking into a Pass and ID Office.

Common Access Card Problems
There are some problems that can arise when using a CAC. These issues include problems with online applications and navigating the DoD SAFE system. Fortunately, some steps can be taken to resolve these issues.
If you are having trouble accessing online applications, try restarting your computer and reinstalling the application. You may also try clearing your browser cookies and cache. If this does not work, try contacting the application provider.
Another issue that many CAC users face is problems with online security. This can be caused by expired or revoked certificates. You can try contacting the ID card office to see if they can fix this problem for you.
CACs can also suffer from problems due to wear and tear. It is important to clean your CAC regularly, especially if you use it frequently. You can clean the gold contacts on the ICC with solvents or a pencil eraser. Also, keep your CAC in a secure place, as it can be easily damaged if it is not properly secured.
One of the most common problems with the CAC is that it may need help logging in to DOD Safe. This is usually due to a corrupted or outdated certificate. It is important to fix these errors quickly, as they can be a major security risk. To do this, you can either contact the ID card office or use a different browser to log in.
Another common problem is that you may not be able to sign a document with your CAC. Many things, including an expired or revoked certificate, a lack of PKI trust, or an invalid signature template can cause this. You can try using a different browser or clearing your SSL sessions to fix this.

